Le modèle H0
Lors d'un test d'hypothèses, l'expérimentateur doit choisir entre 2 hypothèses H0 et H1. La statistique lui fournit un outil de décision basé sur les probabilités.
Si le modèle H0 est correct (modèle H0), 2 zones de probabilité sont définies
- alpha (ou erreur de type I): la probabilité de considérer la moyenne observée comme non conforme ou zone d'événements peu probables sous H0
- 1-alpha (ou confiance): la probabilité de considérer la moyenne observée comme conforme ou zone d'événements probables sous H0
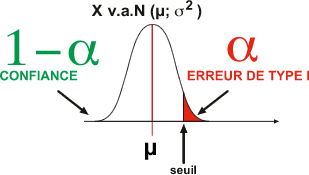
Si la moyenne observée est comprise dans la zone alpha, l'expérimentateur peut tirer une conclusion:
1. Voir un effet qui n'existe pas:
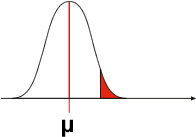
TOUS LES INDIVIDUS SOUS CETTE COURBE SONT CONFORMES
Si la moyenne observée de l'échantillon est comprise dans la zone alpha, cela peut signifier que l'échantillon est constitué fortuitement d'individus normaux dont la taille est exceptionnelle. La moyenne ainsi obtenue est peu probable mais toujours possible sous la courbe. Dans ce cas, l'expérimentateur va conclure erronément que l'échantillon n'appartient pas à la population centrée sur µ.
2. Voir un effet qui existe:
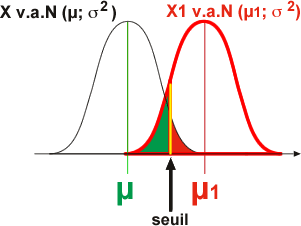
Si la moyenne observée de l'échantillon est comprise dans la zone alpha, cela peut signifier aussi que l'échantillon est constitué d'individus appartenant à une population de moyenne (µ1) distincte de µ (en rouge: cas où il existe une population centrée sur une moyenne µ1 plus grande que µ). L'expérimentateur en conclut que si il observe une telle moyenne c'est qu'elle provient d'une autre distribution (par exemple centrée sur µ1) où cette valeur est beaucoup plus probable.
- Version imprimable
- Vous devez vous identifier ou créer un compte pour écrire des commentaires